Difference between revisions of "Networking/Bandwidth Load and Compression"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
* This is the data transfer rate. | * This is the data transfer rate. | ||
| − | * Usually measured in | + | * Usually measured in Kbps(Kilobits per second). |
[[File:bandwidth3.png|500px]] | [[File:bandwidth3.png|500px]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* Used to reduce storage in hardware. | * Used to reduce storage in hardware. | ||
| − | * Video compression are usually H.264B, H.264, H.265H | + | * Video compression are usually H.264B, H.264, H.265H, and H.265. |
| + | * For more information on H.265 vs H.264, visit [[Troubleshoot/H264_vs_H265|here]]. | ||
| + | * H.264H use more complex encoding algorithms and will produce better quality video at an equivalent transfer rate. | ||
| + | * Baseline profile is easier to decode, but Main and High profiles offer better compression and therefore use less bandwidth to achieve the same quality stream | ||
| − | [[File:Compression1.jpg]] | + | [[File:Compression1.jpg|500px]] |
[[Category:Troubleshoot]] | [[Category:Troubleshoot]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:39, 22 June 2016
Bandwidth, Load, and Compression
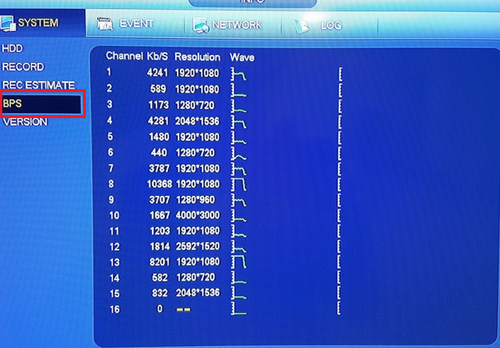
Bandwidth
- This is the data transfer rate.
- Usually measured in Kbps(Kilobits per second).
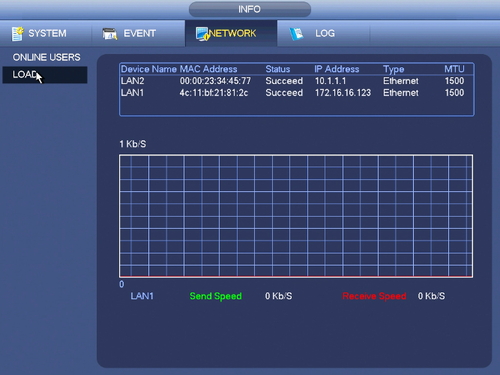
Load
- A high load would be compressing H.265 since it is compressing at a harder algorithm.
- H.264b would be low load since it take less CPU power to compress it.
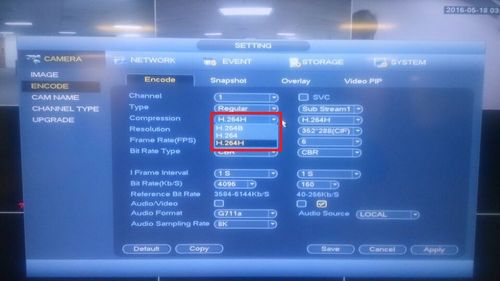
Compression
- Used to reduce storage in hardware.
- Video compression are usually H.264B, H.264, H.265H, and H.265.
- For more information on H.265 vs H.264, visit here.
- H.264H use more complex encoding algorithms and will produce better quality video at an equivalent transfer rate.
- Baseline profile is easier to decode, but Main and High profiles offer better compression and therefore use less bandwidth to achieve the same quality stream