Difference between revisions of "Troubleshoot/H264 vs H265"
m |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
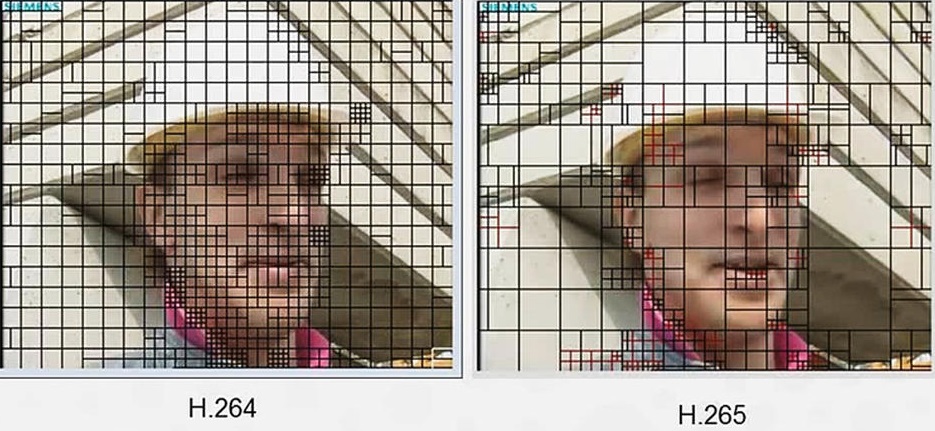
The reason H.265 takes so much processing power to decode is the complexity of how the compression algorithm is written. Also keep in mind that resolutions of 4k to 8k also increasing the load a processor has to decode. The upside to this is the video files essentially can be saved at smaller sizes compared to h.264 | The reason H.265 takes so much processing power to decode is the complexity of how the compression algorithm is written. Also keep in mind that resolutions of 4k to 8k also increasing the load a processor has to decode. The upside to this is the video files essentially can be saved at smaller sizes compared to h.264 | ||
[[File:hevcvsavc002.jpg]] | [[File:hevcvsavc002.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Troubleshoot]] | [[Category:Troubleshoot]] | ||
| + | [[Category:IP Camera]] | ||
| + | [[Category:NVR]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Record Setup]] | ||
Revision as of 21:09, 25 May 2016
H.264 vs. H.265
H.265
- Known as High Efficiency Video Coding(HEVC).
- Successor to H.264 (MPEG-4).
- Saves 44-59% bandwidth and HDD than H.264.
- Saves 40-50% Bitrate.
- Supports up to 8K.
- Bigger resolutions are compressed better
- Takes more processing power (up to 10x)
H.264
- Known as Advance Video Coding(AVC).
- Successor to MPEG-2 Part.
- Supports up to 4K.
- Current mainstream video compression format.
- Widely used in Blu-ray disc and other internet sources.
Real time test
The graph below demonstrates bandwidth differences between HEVC (H.265) vs AVC (H.264) in a real time.
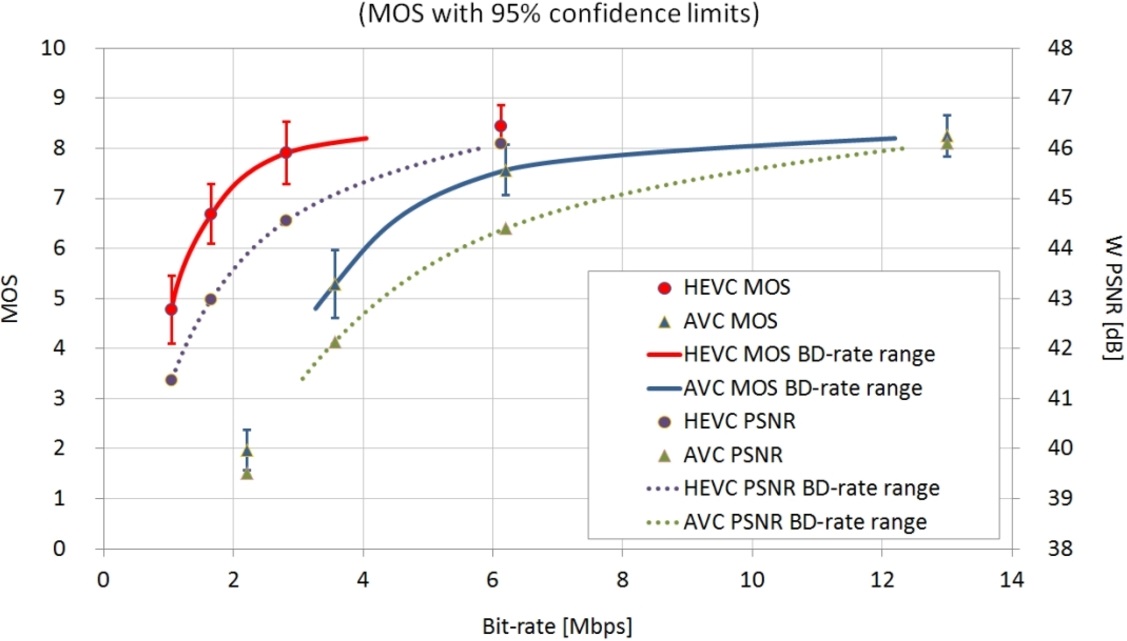
The reason H.265 takes so much processing power to decode is the complexity of how the compression algorithm is written. Also keep in mind that resolutions of 4k to 8k also increasing the load a processor has to decode. The upside to this is the video files essentially can be saved at smaller sizes compared to h.264


