SNMP
Contents
SNMP
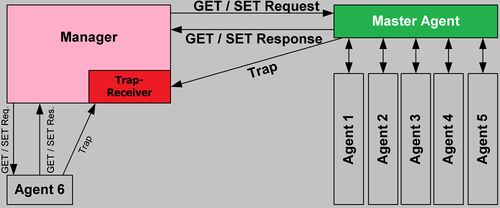
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet-standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behavior. Devices that typically support SNMP include routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, modem racks and more. In this case it will be IP Cameras, NVR's, and other network devices with the option to enable this protocol. SNMP allows the communication between the network management work station software (or enterprise switch with SNMP management) and the proxy of the managed device. Please install the software such as MG MibBrowser 8.0c, MG-Soft MIB suite, iReasoning MIB Browser, or just about any MIB browser that is in use today to establish the SNMP service before you use this function. You will need to reboot the device to activate the new setup. Additionally you can use other programs such as Solar Winds Real-Time Bandwidth Monitor to externally monitor the bandwidth on the active network.
There are 3 versions of SNMP:
- SNMP Version 1:
SNMPv1 is the initial implementation of the SNMP protocol. SNMPv1 operates over protocols such as User Datagram Protocol (UDP), Internet Protocol (IP), OSI Connectionless Network Service (CLNS), AppleTalk Datagram-Delivery Protocol (DDP), and Novell Internet Packet Exchange (IPX). SNMPv1 is widely used and is the de facto network-management protocol in the Internet community.
- SNMP Version 2:
SNMPv2 (RFC 1441–RFC 1452), revises version 1 and includes improvements in the areas of performance, security, confidentiality, and manager-to-manager communications. It introduced GetBulkRequest, an alternative to iterative GetNextRequests for retrieving large amounts of management data in a single request. However, the new party-based security system in SNMPv2, viewed by many as overly complex, was not widely accepted.[8] This version of SNMP reached the Proposed Standard level of maturity, but was deemed obsoleted by later versions
- SNMP Version 3:
SNMPv3 makes no changes to the protocol aside from the addition of cryptographic security, it looks much different due to new textual conventions, concepts, and terminology
Enabling SNMPv1-3 on Dahua Devices
1. To enable SNMP protocol on your NVR or IP Camera please log in via the web interface or the user interface (nvr only) with an administrator account.
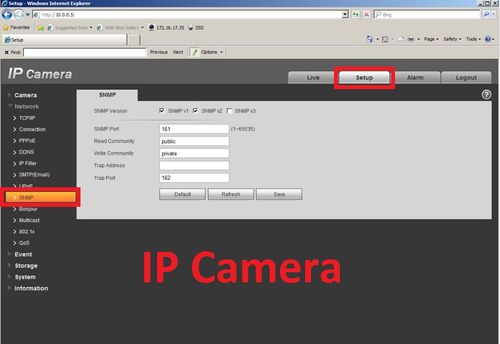
2. On the web interface Select the setup tab, then click on network, and then SNMP
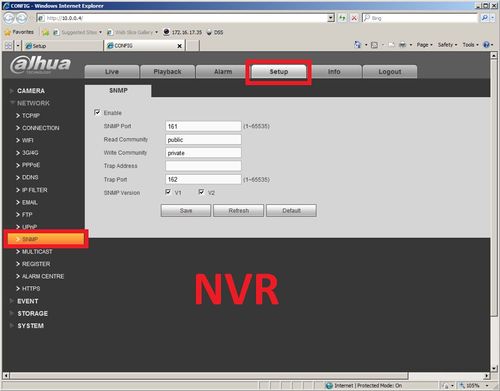
3. On this page you will define the SNMP version 1, 2, or 3 settings.
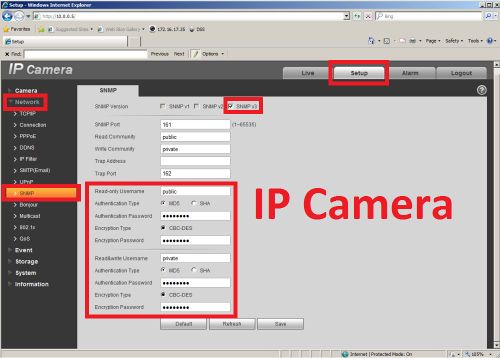
4. Check SNMP v1, device only process v1 info, Check SNMP v2, device only process v2 info, Check SNMP v3, can set username, password and
encryption method.
5.At this point use these settings to calibrate your IPC or NVR with the SNMP server. For this demo I will use Solar Winds to capture information about the device.
Additional information:
-SNMP port: the listening port of the proxy program of the device. It's the UDP port not a TCP port and the value ranges from 1 to 65535, the default value is 161.
-Community: a string command between management and proxy, define a proxy, and a manager’s authentication.
-Read community: Read-only access to all SNMP targets, default is public. (Note: Only number, letter, _, and – supported.)
-Write community: Read/write access to all SNMP targets, default is private. (Note: Only number, letter, _, and – supported.)
-Trap address: The destination address of the Trap information from the proxy program of the device.
-Trap SNMP: The trap proxy message sent to an admin as the important event notice or status changes.
-Trap Address: Address where to send Trap message.
-Trap Port: Port which send Trap message, default is 162, range 1~65535
-You may select MD5 or SHA, the default is MD5
-Authentication Password: Password not less than 8 characters. The encryption default is CBC-DES.
-Port conflict occurs when SNMP port and Trap port are the same.
Resources
Solar Winds SNMP Monitoring & Management MG-SOFT MIB Browser, MIB Builder iReasoning MIB Browser