Troubleshoot/What Is Focal Length Aperture Gain Angle of View
What is Focal Length, Aperture, Gain, Angle of View?
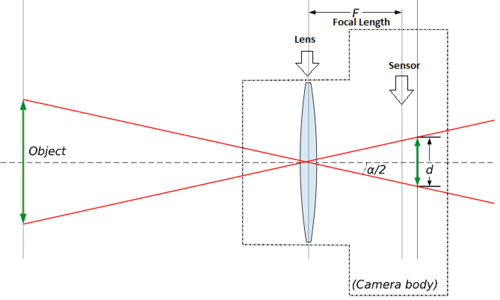
Focal Length
- The focal length of a lens is the distance, in millimeters, between the sensor (focal plane) and the optical center of the lens. It is not a measurement of the actual length of a lens, but a calculation of an optical distance from the point where light rays converge to form a sharp image of an object to the digital sensor or 35mm film at the focal plane in the camera. The focal length of a lens is determined when the lens is focused at infinity. The focal length tells us the angle of view—how much of the scene will be captured—and the magnification—how large individual elements will be. The longer the focal length, the narrower the angle of view and the higher the magnification. The shorter the focal length, the wider the angle of view and the lower the magnification.
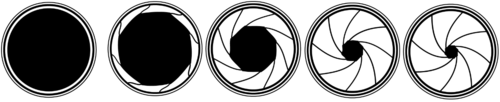
Aperture
- Aperture refers to the opening of a lens's diaphragm through which light passes. It is calibrated in f/stops and is generally written as numbers such as 1.4, 2, 2.8, 4, 5.6, 8, 11 and 16. The lower f/stops give more exposure because they represent the larger apertures, while the higher f/stops give less exposure because they represent smaller apertures. This may seem a little contradictory at first but will become clearer as you take pictures at varying f/stops. The lower the f/stop—the larger the opening in the lens—the less depth of field—the blurrier the background. The higher the f/stop—the smaller the opening in the lens—the greater the depth of field—the sharper the background.
Gain
- Gain is an electronic way to boost the brightness of your video images. When shooting in low light conditions (e.g. at night) the iris will be fully open at f1.6 but, the camera may still needs more light to produce a picture. If you cannot light the scene then the only way to brighten the image is to electronically boost it with GAIN. The great thing about gain is that you will be able to see in the dark.
Note the examples from below.
Angle of View
- The viewing angle is akin to the “portion of the scene” that the lens can capture. Viewing angle is measured in degrees. The more angular your lens is, the greater portion of the scene you can capture with your lens. The more you zoom into a scene, the lower portion of the image that will be captured in a photo. Lenses are categorized and marketed based upon their focal length. However the really important measure of a lens is the angle of view. Every viewing angle corresponds to a specific focal length.
For example, take a look at the images below: